Smoking (food) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
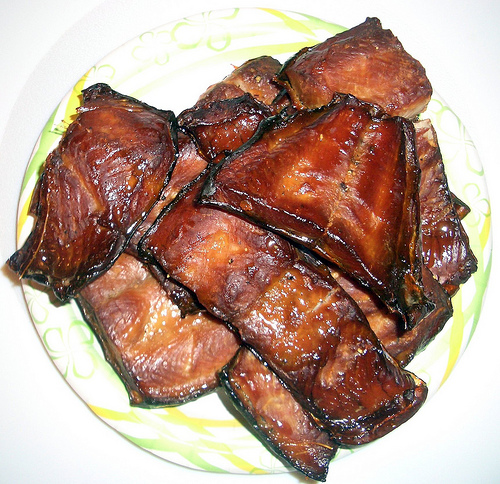

 Smoking is the process of flavoring, browning, cooking, or preserving food by exposing it to smoke from burning or smoldering material, most often wood. Meat, fish, and '' lapsang souchong'' tea are often smoked.
In Europe, alder is the traditional smoking wood, but oak is more often used now, and
Smoking is the process of flavoring, browning, cooking, or preserving food by exposing it to smoke from burning or smoldering material, most often wood. Meat, fish, and '' lapsang souchong'' tea are often smoked.
In Europe, alder is the traditional smoking wood, but oak is more often used now, and
Briefing: Smoked Food
The Herald, 2/19/2002''Janes, Hilly
The Independent 10/10/2001 As simple dwellings lacked chimneys, these structures would probably have become very smoky. It is supposed that early humans would hang meat up to dry and out of the way of pests, thus accidentally becoming aware that meat that was stored in smoky areas acquired a different flavor, and was better preserved than meat that simply dried out. This process was later combined with pre-curing the food in salt or salty brine, resulting in a remarkably effective preservation process that was adapted and developed by numerous cultures around the world. Until the modern era, smoking was of a more "heavy duty" nature as the main goal was to preserve the food. Large quantities of salt were used in the curing process and smoking times were quite long, sometimes involving days of exposure. The advent of modern transportation made it easier to transport food products over long distances and the need for the time and material intensive heavy salting and smoking declined. Smoking became more of a way to flavor than to preserve food. In 1939 a device called the Torry Kiln was invented at the

 The main characteristics of the offset smoker are that the cooking chamber is usually cylindrical in shape, with a shorter, smaller diameter cylinder attached to the bottom of one end for a firebox. To cook the meat, a small fire is lit in the firebox, where airflow is tightly controlled. The heat and smoke from the fire are drawn through a connecting pipe or opening into the cooking chamber.
The heat and smoke cook and flavor the meat before escaping through an exhaust vent at the opposite end of the cooking chamber. Most manufacturers' models are based on this simple but effective design, and this is what most people picture when they think of a "BBQ smoker". Even large capacity commercial units use this same basic design of a separate, smaller fire box and a larger cooking chamber.
The main characteristics of the offset smoker are that the cooking chamber is usually cylindrical in shape, with a shorter, smaller diameter cylinder attached to the bottom of one end for a firebox. To cook the meat, a small fire is lit in the firebox, where airflow is tightly controlled. The heat and smoke from the fire are drawn through a connecting pipe or opening into the cooking chamber.
The heat and smoke cook and flavor the meat before escaping through an exhaust vent at the opposite end of the cooking chamber. Most manufacturers' models are based on this simple but effective design, and this is what most people picture when they think of a "BBQ smoker". Even large capacity commercial units use this same basic design of a separate, smaller fire box and a larger cooking chamber.
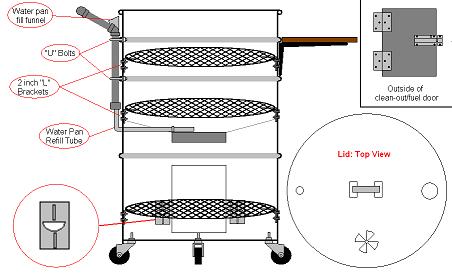 The upright drum smoker (also referred to as an ugly drum smoker or UDS) is exactly what its name suggests; an upright steel drum that has been modified for the purpose of pseudo-indirect hot smoking. There are many ways to accomplish this, but the basics include the use of a complete steel drum, a basket to hold charcoal near the bottom, and cooking rack (or racks) near the top; all covered by a vented lid of some sort. They have been built using many different sizes of steel drums, such as , , and for example, but the most popular size is the common 55-gallon drum.
This design is similar to smoking with indirect heat due to the distance from the coals and the racks, which is typically . The temperatures used for smoking are controlled by limiting the amount of air intake at the bottom of the drum, and allowing a similar amount of exhaust out of vents in the lid. UDSs are very efficient with fuel consumption and flexible in their abilities to produce proper smoking conditions, with or without the use of a water pan or drip pan.
The upright drum smoker (also referred to as an ugly drum smoker or UDS) is exactly what its name suggests; an upright steel drum that has been modified for the purpose of pseudo-indirect hot smoking. There are many ways to accomplish this, but the basics include the use of a complete steel drum, a basket to hold charcoal near the bottom, and cooking rack (or racks) near the top; all covered by a vented lid of some sort. They have been built using many different sizes of steel drums, such as , , and for example, but the most popular size is the common 55-gallon drum.
This design is similar to smoking with indirect heat due to the distance from the coals and the racks, which is typically . The temperatures used for smoking are controlled by limiting the amount of air intake at the bottom of the drum, and allowing a similar amount of exhaust out of vents in the lid. UDSs are very efficient with fuel consumption and flexible in their abilities to produce proper smoking conditions, with or without the use of a water pan or drip pan.
p. 9. is a variation of the upright drum smoker. It uses charcoal or wood to generate smoke and heat, and contains a water bowl between the fire and the cooking grates. The water bowl serves to maintain optimal smoking temperatures and also adds humidity to the smoke chamber. It also creates an effect in which the water vapor and smoke condense together, which adds flavor to smoked foods. In addition, the bowl catches any drippings from the meat that may cause a flare-up. Vertical water smokers are extremely temperature stable and require very little adjustment once the desired temperature has been reached. Because of their relatively low cost and stable temperature, they are sometimes used in barbecue competitions where propane and electric smokers are not allowed.
 A
A
 In this method the firebox is a narrow trench cut down a slope pointing into the prevailing wind. The middle part of the trench is covered over to make it into a tunnel. At the upper end of the trench is a vertical framework covered to form a chimney within which is placed the rack of foodstuff. At the lower upwind end of the trench is lit a small smokey fire, and sustained day and night until the foodstuff is cured.
In this method the firebox is a narrow trench cut down a slope pointing into the prevailing wind. The middle part of the trench is covered over to make it into a tunnel. At the upper end of the trench is a vertical framework covered to form a chimney within which is placed the rack of foodstuff. At the lower upwind end of the trench is lit a small smokey fire, and sustained day and night until the foodstuff is cured.
 Smoke is both an antimicrobial and
Smoke is both an antimicrobial and


 Some of the more common smoked foods and beverages include:
; Beverages
*'' Lapsang souchong'' tea leaves are smoked and dried over pine or cedar fires
*
Some of the more common smoked foods and beverages include:
; Beverages
*'' Lapsang souchong'' tea leaves are smoked and dried over pine or cedar fires
*

 Smoking is the process of flavoring, browning, cooking, or preserving food by exposing it to smoke from burning or smoldering material, most often wood. Meat, fish, and '' lapsang souchong'' tea are often smoked.
In Europe, alder is the traditional smoking wood, but oak is more often used now, and
Smoking is the process of flavoring, browning, cooking, or preserving food by exposing it to smoke from burning or smoldering material, most often wood. Meat, fish, and '' lapsang souchong'' tea are often smoked.
In Europe, alder is the traditional smoking wood, but oak is more often used now, and beech
Beech (''Fagus'') is a genus of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to temperate Europe, Asia, and North America. Recent classifications recognize 10 to 13 species in two distinct subgenera, ''Engleriana'' and ''Fagus''. The ''Engle ...
to a lesser extent. In North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
, hickory
Hickory is a common name for trees composing the genus ''Carya'', which includes around 18 species. Five or six species are native to China, Indochina, and India (Assam), as many as twelve are native to the United States, four are found in Mexi ...
, mesquite, oak, pecan, alder, maple, and fruit-tree woods, such as apple, cherry
A cherry is the fruit of many plants of the genus ''Prunus'', and is a fleshy drupe (stone fruit).
Commercial cherries are obtained from cultivars of several species, such as the sweet ''Prunus avium'' and the sour ''Prunus cerasus''. The nam ...
, and plum
A plum is a fruit of some species in ''Prunus'' subg. ''Prunus'.'' Dried plums are called prunes.
History
Plums may have been one of the first fruits domesticated by humans. Three of the most abundantly cultivated species are not found i ...
, are commonly used for smoking. Other biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bi ...
besides wood can also be employed, sometimes with the addition of flavoring ingredients. Chinese tea-smoking uses a mixture of uncooked rice, sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double ...
, and tea, heated at the base of a wok.
Some North American ham and bacon
Bacon is a type of salt-cured pork made from various cuts, typically the belly or less fatty parts of the back. It is eaten as a side dish (particularly in breakfasts), used as a central ingredient (e.g., the bacon, lettuce, and tomato sand ...
makers smoke their products over burning corncob
A corncob, also called corn cob, cob of corn or corn on the cob, is the central core of an ear of corn (also known as maize). It is the part of the ear on which the kernels grow. The ear is also considered a "cob" or "pole" but it is not fully ...
s. Peat is burned to dry and smoke the barley malt
Malt is germinated cereal grain that has been dried in a process known as " malting". The grain is made to germinate by soaking in water and is then halted from germinating further by drying with hot air.
Malted grain is used to make beer, wh ...
used to make Scotch whisky
Scotch whisky (; sco, Scots whisky/whiskie, whusk(e)y; often simply called whisky or Scotch) is malt whisky or grain whisky (or a blend of the two), made in Scotland.
All Scotch whisky was originally made from malted barley. Commercial distil ...
and some beers. In New Zealand, sawdust from the native manuka (tea tree) is commonly used for hot smoking fish
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is burned and the resulting smoke is typically breathed in to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, which have bee ...
. In Iceland, dried sheep dung is used to cold-smoke fish, lamb, mutton and whale.
Historically, farms in the Western world included a small building termed the " smokehouse", where meats could be smoked and stored. This was generally well separated from other buildings both because of the fire danger and because of the smoke emanations; the smoking of food could possibly introduce polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons which may lead to an increased risk of some types of cancer; however, this association is still being debated.
Smoking can be done in four ways: cold smoking, warm smoking, hot smoking, and through the employment of a smoke flavoring, such as liquid smoke. However, these methods of imparting smoke only affect the food surface, and are unable to preserve food, thus, smoking is paired with other microbial hurdles, such as chilling and packaging, to extend food shelf-life.
History
The smoking of food likely dates back to thepaleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός ''palaios'', "old" and λίθος ''lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone too ...
era.Briefing: Smoked Food
The Herald, 2/19/2002''Janes, Hilly
The Independent 10/10/2001 As simple dwellings lacked chimneys, these structures would probably have become very smoky. It is supposed that early humans would hang meat up to dry and out of the way of pests, thus accidentally becoming aware that meat that was stored in smoky areas acquired a different flavor, and was better preserved than meat that simply dried out. This process was later combined with pre-curing the food in salt or salty brine, resulting in a remarkably effective preservation process that was adapted and developed by numerous cultures around the world. Until the modern era, smoking was of a more "heavy duty" nature as the main goal was to preserve the food. Large quantities of salt were used in the curing process and smoking times were quite long, sometimes involving days of exposure. The advent of modern transportation made it easier to transport food products over long distances and the need for the time and material intensive heavy salting and smoking declined. Smoking became more of a way to flavor than to preserve food. In 1939 a device called the Torry Kiln was invented at the
Torry Research Station
The Central Science Laboratory (CSL) was an executive agency of the UK government branch, the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (DEFRA). It is now part of the Food and Environment Research Agency, which is in turn part of DEFRA. ...
in Scotland. The kiln allowed for uniform mass-smoking and is considered the prototype for all modern large-scale commercial smokers. Although refinements in technique and advancements in technology have made smoking much easier, the basic steps involved remain essentially the same today as they were hundreds if not thousands of years ago.
by method of application
Cold smoking
Cold smoking differs from hot smoking in that the food remains raw, rather than cooked, throughout the smoking process. Smokehouse temperatures for cold smoking are typically done between . In this temperature range, foods take on a smoked flavor, but remain relatively moist. Cold smoking does not cook foods, and as such, meats should be fully cured before cold smoking. Cold smoking can be used as a flavor enhancer for items such ascheese
Cheese is a dairy product produced in wide ranges of flavors, textures, and forms by coagulation of the milk protein casein. It comprises proteins and fat from milk, usually the milk of cows, buffalo, goats, or sheep. During production, ...
or nuts
Nut often refers to:
* Nut (fruit), fruit composed of a hard shell and a seed, or a collective noun for dry and edible fruits or seeds
* Nut (hardware), fastener used with a bolt
Nut or Nuts may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Com ...
, along with meats such as chicken breasts, beef, pork chops, salmon, scallop
Scallop () is a common name that encompasses various species of marine bivalve mollusks in the taxonomic family Pectinidae, the scallops. However, the common name "scallop" is also sometimes applied to species in other closely related families ...
s, and steak. The item is often hung in a dry environment first to develop a pellicle
Pellicle may refer to:
* Pellicle (biology), a thin layer supporting the cell membrane in various protozoa
* Pellicle mirror, a thin plastic membrane which may be used as a beam splitter or protective cover in optical systems
*Pellicle (dental), ...
; it can then be cold smoked up to several days to ensure it absorbs the smoke flavor. Some cold smoked foods are baked, grilled, steamed, roasted, or sautéed before eating.
Cold smoking meats is not something that should be attempted at home, according to the US National Center for Home Food Preservation: "Most food scientists cannot recommend cold-smoking methods because of the inherent risks."
Cold smoking meats should only be attempted by personnel certified in HACCP ..to ensure that it is safely prepared.
Warm smoking
Warm smoking exposes foods to temperatures of .Hot smoking
Hot smoking exposes the foods to smoke and heat in a controlled environment such as a smoker oven or smokehouse. Hot smoking requires the use of a smoker which generates heat either from a charcoal base, heated element within the smoker or from a stove-top or oven; food is hot smoked by cooking and flavored with wood smoke simultaneously. Like cold smoking, the item may be hung first to develop apellicle
Pellicle may refer to:
* Pellicle (biology), a thin layer supporting the cell membrane in various protozoa
* Pellicle mirror, a thin plastic membrane which may be used as a beam splitter or protective cover in optical systems
*Pellicle (dental), ...
; it is then smoked from 1 hour to as long as 24 hours. Although foods that have been hot smoked are often reheated or further cooked, they are typically safe to eat without further cooking. Hams and ham hocks are fully cooked once they are properly smoked, and they can be eaten as is without any further preparation. Hot smoking usually occurs within the range of . When food is smoked within this temperature range, foods are fully cooked, moist, and flavorful. If the smoker is allowed to get hotter than , the foods can shrink excessively, buckle, or even split. Smoking at high temperatures also reduces yield, as both moisture and fat are cooked away.
Liquid smoke
Liquid smoke, a product derived from smoke compounds in water, is applied to foods through spraying or dipping.Smoke roasting
Smoke-roasting refers to any process that has the attributes of both roasting and smoking. This smoking method is sometimes referred to as barbecuing or pit-roasting. It may be done in a smoke-roaster, a closed wood-fired oven, or a barbecue pit, any smoker that can reach above , or in a conventional oven by placing a pan filled with hardwood chips on the floor of the oven so that the chips can smolder and produce a smoke-bath. InNorth America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
, this smoking method is commonly referred to as "barbecuing", "pit baking", or "pit roasting".
Types by biomass
Wood smoke

Hardwood
Hardwood is wood from dicot trees. These are usually found in broad-leaved temperate and tropical forests. In temperate and boreal latitudes they are mostly deciduous, but in tropics and subtropics mostly evergreen. Hardwood (which comes from ...
s are made up mostly of three materials: cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidity ...
. Cellulose and hemicellulose are the basic structural material of the wood cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
; lignin acts as a kind of cell-bonding glue. Some softwood
file:Pinus sylvestris wood ray section 1 beentree.jpg, Scots Pine, a typical and well-known softwood
Softwood is wood from gymnosperm trees such as conifers. The term is opposed to hardwood, which is the wood from angiosperm trees. The main diff ...
s, especially pines and fir
Firs (''Abies'') are a genus of 48–56 species of evergreen coniferous trees in the family (biology), family Pinaceae. They are found on mountains throughout much of North America, North and Central America, Europe, Asia, and North Africa. The ...
s, hold significant quantities of resin, which produces a harsh-tasting soot when burned; these woods are not often used for smoking.
Cellulose and hemicellulose are aggregate sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double ...
molecules; when burnt, they effectively caramelize, producing carbonyls, which provide most of the color components and sweet, flowery, and fruity aromas. Lignin, a highly complex arrangement of interlocked phenolic molecules, also produces a number of distinctive aromatic elements when burnt, including smoky, spicy, and pungent compounds such as guaiacol, phenol, and syringol, and sweeter scents such as the vanilla-scented vanillin and clove
Cloves are the aromatic flower buds of a tree in the family Myrtaceae, ''Syzygium aromaticum'' (). They are native to the Maluku Islands (or Moluccas) in Indonesia, and are commonly used as a spice, flavoring or fragrance in consumer products, ...
-like isoeugenol. Guaiacol is the phenolic compound most responsible for the "smoky" taste, while syringol is the primary contributor to smoky aroma. Wood also contains small quantities of proteins, which contribute roasted flavors. Many of the odor compounds in wood smoke, especially the phenolic compounds, are unstable, dissipating after a few weeks or months.
A number of wood smoke compounds act as preservatives. Phenol and other phenolic compounds in wood smoke are both antioxidant
Antioxidants are compounds that inhibit oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce free radicals. This can lead to polymerization and other chain reactions. They are frequently added to industrial products, such as fuels and lubricant ...
s, which slow rancidification of animal fats, and antimicrobials, which slow bacterial growth. Other antimicrobials in wood smoke include formaldehyde, acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component ...
, and other organic acids, which give wood smoke a low pH—about 2.5. Some of these compounds are toxic to people as well, and may have health effects in the quantities found in cooking applications.
Since different species of trees have different ratios of components, various types of wood do impart a different flavor to food. Another important factor is the temperature at which the wood burns. High-temperature fires see the flavor molecules broken down further into unpleasant or flavorless compounds. The optimal conditions for smoke flavor are low, smoldering temperatures between . This is the temperature of the burning wood itself, not of the smoking environment, which uses much lower temperatures. Woods that are high in lignin content tend to burn hot; to keep them smoldering requires restricted oxygen supplies or a high moisture content. When smoking using wood chips or chunks, the combustion temperature is often raised by soaking the pieces in water before placing them on a fire.
Types of smokers
Offset
 The main characteristics of the offset smoker are that the cooking chamber is usually cylindrical in shape, with a shorter, smaller diameter cylinder attached to the bottom of one end for a firebox. To cook the meat, a small fire is lit in the firebox, where airflow is tightly controlled. The heat and smoke from the fire are drawn through a connecting pipe or opening into the cooking chamber.
The heat and smoke cook and flavor the meat before escaping through an exhaust vent at the opposite end of the cooking chamber. Most manufacturers' models are based on this simple but effective design, and this is what most people picture when they think of a "BBQ smoker". Even large capacity commercial units use this same basic design of a separate, smaller fire box and a larger cooking chamber.
The main characteristics of the offset smoker are that the cooking chamber is usually cylindrical in shape, with a shorter, smaller diameter cylinder attached to the bottom of one end for a firebox. To cook the meat, a small fire is lit in the firebox, where airflow is tightly controlled. The heat and smoke from the fire are drawn through a connecting pipe or opening into the cooking chamber.
The heat and smoke cook and flavor the meat before escaping through an exhaust vent at the opposite end of the cooking chamber. Most manufacturers' models are based on this simple but effective design, and this is what most people picture when they think of a "BBQ smoker". Even large capacity commercial units use this same basic design of a separate, smaller fire box and a larger cooking chamber.
Upright drum
Vertical water
A vertical water smoker (also referred to as a bullet smoker because of its shape)Backyard Grilling: For Your Grill, Smoker, Turkey Fryer and More – Kate Fiduccia, Teresa Marronep. 9. is a variation of the upright drum smoker. It uses charcoal or wood to generate smoke and heat, and contains a water bowl between the fire and the cooking grates. The water bowl serves to maintain optimal smoking temperatures and also adds humidity to the smoke chamber. It also creates an effect in which the water vapor and smoke condense together, which adds flavor to smoked foods. In addition, the bowl catches any drippings from the meat that may cause a flare-up. Vertical water smokers are extremely temperature stable and require very little adjustment once the desired temperature has been reached. Because of their relatively low cost and stable temperature, they are sometimes used in barbecue competitions where propane and electric smokers are not allowed.
Propane
 A
A propane
Propane () is a three-carbon alkane with the molecular formula . It is a gas at standard temperature and pressure, but compressible to a transportable liquid. A by-product of natural gas processing and petroleum refining, it is commonly used a ...
smoker is designed to allow the smoking of meat in a somewhat more temperature controlled environment. The primary differences are the sources of heat and of the smoke. In a propane smoker, the heat is generated by a gas burner directly under a steel or iron box containing the wood or charcoal that provides the smoke. The steel box has few vent holes, on the top of the box only. By starving the heated wood of oxygen, it smokes instead of burning. Any combination of woods and charcoal may used. This method uses much less wood but does require propane fuel.
Smoke box
This more traditional method uses a two-box system: a fire box and a food box. The fire box is typically adjacent or under the cooking box, and can be controlled to a finer degree. The heat and smoke from the fire box exhausts into the food box, where it is used to cook and smoke the meat. These may be as simple as an electric heating element with a pan of wood chips placed on it, although more advanced models have finer temperature controls.Electric smokers
The most convenient of the various types of smokers are the insulated electric smokers. These devices house a heating element that can maintain temperatures ranging from that required for a cold smoke all the way up to with little to no intervention from the user. Although wood chunks, pellets, and even in some cases automatically fed wood pucks are used to generate smoke, the amount of flavor obtained is less than traditional wood or charcoal smokers.Trench
 In this method the firebox is a narrow trench cut down a slope pointing into the prevailing wind. The middle part of the trench is covered over to make it into a tunnel. At the upper end of the trench is a vertical framework covered to form a chimney within which is placed the rack of foodstuff. At the lower upwind end of the trench is lit a small smokey fire, and sustained day and night until the foodstuff is cured.
In this method the firebox is a narrow trench cut down a slope pointing into the prevailing wind. The middle part of the trench is covered over to make it into a tunnel. At the upper end of the trench is a vertical framework covered to form a chimney within which is placed the rack of foodstuff. At the lower upwind end of the trench is lit a small smokey fire, and sustained day and night until the foodstuff is cured.
Commercial smokehouse
Commercial smokehouses, mostly made from stainless steel, have independent systems for smoke generation and cooking. Smoke generators use friction, an electric coil or a small flame to ignite sawdust on demand. Heat from steam coils or gas flames is balanced with live steam or water sprays to control the temperature and humidity. Elaborate air handling systems reduce hot or cold spots, to reduce variation in the finished product. Racks on wheels or rails are used to hold the product and facilitate movement.Pellet smokers
A pellet smoker is a temperature controlled smoker that burns wood pellets made of dried out sawdust, about an inch long and 1/4 inch wide. The wood pellets are stored in a gravity-fed hopper that feeds into a motor controlled auger by the temperature regulator. This auger pushes the pellets into the fire pot. An ignition rod within the auger ignites the pellets where a combustion fan keeps them smouldering. The motor and the combustion fan regulate the temperature of the smoker by feeding it more pellets and increasing airflow in the auger. Above the auger is a heat shield to disperse the direct heat before it reaches the heat box to allow the wood smoke to keep the heat box at an even temperature throughout. The heat sensor inside the heat box relays the current temperature inside the box back to the temperature regulator that controls the fan speed and pellet hopper motor, which either increase or decrease the amount of pellets in the auger or the amount of air available to the fire to maintain the desired temperature for the cook. The popularity of this type of smokers is on the rise after many BBQ pit-masters started using them for competition barbeque.Preservation
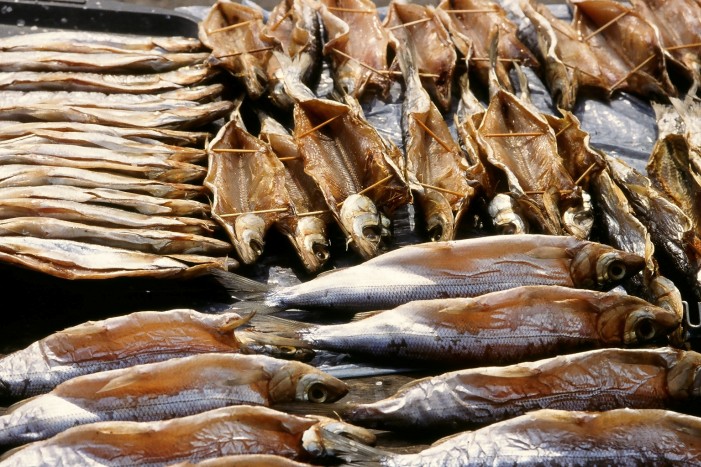
 Smoke is both an antimicrobial and
Smoke is both an antimicrobial and antioxidant
Antioxidants are compounds that inhibit oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce free radicals. This can lead to polymerization and other chain reactions. They are frequently added to industrial products, such as fuels and lubricant ...
, however it is insufficient alone for preserving food as smoke does not penetrate far into meat or fish; it is thus typically combined with salt-curing or drying.
Smoking is especially useful for oily fish, as its antioxidant
Antioxidants are compounds that inhibit oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce free radicals. This can lead to polymerization and other chain reactions. They are frequently added to industrial products, such as fuels and lubricant ...
properties inhibit surface fat rancidification and delay interior fat exposure to degrading oxygen. Some heavily salted, long-smoked fish can keep without refrigeration for weeks or months.
Artificial smoke flavoring (such as liquid smoke) can be purchased to mimic smoking's flavor, but not its preservative qualities.
Competitive smoking
Competition BBQ Smoking is becoming increasingly popular among smoking enthusiasts, especially in the Southern American States, where BBQ enthusiasts come together over a weekend to cook various cuts of meat such as a whole hog or beef brisket to become the best at BBQ. Organisations such as Kansas City Barbeque Society run competitions all over America.Health concerns
Regularly consuming smoked meats and fish may increase the risk of several types of cancer andcardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, h ...
.
List of smoked foods and beverages


 Some of the more common smoked foods and beverages include:
; Beverages
*'' Lapsang souchong'' tea leaves are smoked and dried over pine or cedar fires
*
Some of the more common smoked foods and beverages include:
; Beverages
*'' Lapsang souchong'' tea leaves are smoked and dried over pine or cedar fires
*Malt
Malt is germinated cereal grain that has been dried in a process known as " malting". The grain is made to germinate by soaking in water and is then halted from germinating further by drying with hot air.
Malted grain is used to make beer, wh ...
beverages
**The malt used to make whisky
** Rauchbier (smoked beer)
;Fruit and vegetables
* Capsicums: chipotles (smoked, ripe jalapeños), paprika
Paprika ( US , ; UK , ) is a spice made from dried and ground red peppers. It is traditionally made from ''Capsicum annuum'' varietals in the Longum group, which also includes chili peppers, but the peppers used for paprika tend to be milder an ...
* Prunes (dried plum
A plum is a fruit of some species in ''Prunus'' subg. ''Prunus'.'' Dried plums are called prunes.
History
Plums may have been one of the first fruits domesticated by humans. Three of the most abundantly cultivated species are not found i ...
s) can be smoked while drying
*''Wumei'' are smoked plum
A plum is a fruit of some species in ''Prunus'' subg. ''Prunus'.'' Dried plums are called prunes.
History
Plums may have been one of the first fruits domesticated by humans. Three of the most abundantly cultivated species are not found i ...
fruits
*''Iburi-gakko'' are a smoked daikon pickle from Akita Prefecture
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Tōhoku region of Honshu.Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "Provinces and prefectures" in ; "Tōhoku" in . Its population is approximately 966,000 (as of 1 October 2019) and its ge ...
, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
;Meat, fish, and cheese
* Beef
** Pastrami (pickled, spiced and smoked beef brisket)
* Pork
**Bacon
Bacon is a type of salt-cured pork made from various cuts, typically the belly or less fatty parts of the back. It is eaten as a side dish (particularly in breakfasts), used as a central ingredient (e.g., the bacon, lettuce, and tomato sand ...
** Ham
** Bakkwa
* Turkey
* Chicken
* Sausage
** Salami
* Jerky
* Fish
** Eel popular in eastern/northern EuropeAnthony Bourdain. A local's obsession with smoked eel. "No Reservations". http://www.travelchannel.com/video/a-locals-obsession-with-smoked-eel-11676.
** Traditional Grimsby smoked fish (cod and haddock)
** Haddock and Arbroath smokie
The Arbroath smokie is a type of smoked haddock, and is a speciality of the town of Arbroath in Angus, Scotland.
History
The Arbroath smokie is said to have originated in the small fishing village of Auchmithie, three miles northeast of A ...
s (haddock)
** Buckling, kippers and bloater (herring)
** Salmon
**Mackerel
Mackerel is a common name applied to a number of different species of pelagic fish, mostly from the family Scombridae. They are found in both temperate and tropical seas, mostly living along the coast or offshore in the oceanic environment.
...
**Bivalves including oysters and mussel
Mussel () is the common name used for members of several families of bivalve molluscs, from saltwater and Freshwater bivalve, freshwater habitats. These groups have in common a shell whose outline is elongated and asymmetrical compared with other ...
s.
*Egg
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the a ...
( eggs and fish eggs)
*Cheese
Cheese is a dairy product produced in wide ranges of flavors, textures, and forms by coagulation of the milk protein casein. It comprises proteins and fat from milk, usually the milk of cows, buffalo, goats, or sheep. During production, ...
** Adyghe Qwaye (Circassian)
**Gouda
Gouda may refer to:
* Gouda, South Holland, a city in the Netherlands
** Gouda (pottery), style of pottery manufactured in Gouda
** Gouda cheese, type of cheese originally made in and around Gouda
** Gouda railway station
* Gouda, Western Cape, a s ...
** Gruyère
;Other proteins
*Nuts
Nut often refers to:
* Nut (fruit), fruit composed of a hard shell and a seed, or a collective noun for dry and edible fruits or seeds
* Nut (hardware), fastener used with a bolt
Nut or Nuts may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Com ...
* Tofu
;Spices
*Paprika
Paprika ( US , ; UK , ) is a spice made from dried and ground red peppers. It is traditionally made from ''Capsicum annuum'' varietals in the Longum group, which also includes chili peppers, but the peppers used for paprika tend to be milder an ...
* Salt
See also
* Braising *Canning
Canning is a method of food preservation in which food is processed and sealed in an airtight container (jars like Mason jars, and steel and tin cans). Canning provides a shelf life that typically ranges from one to five years, although u ...
* Drying
* Jerky
* List of dried foods
* List of sausage dishes
* List of sausages
This is a list of notable sausages. Sausage is a food usually made from ground meat with a skin around it. Typically, a sausage is formed in a casing traditionally made from intestine, but sometimes synthetic. Some sausages are cooked durin ...
* List of smoked foods
This is a list of smoked foods. Smoking is the process of flavoring, cooking, or preserving food by exposing it to smoke from burning or smoldering material, most often wood. Foods have been smoked by humans throughout history. Meats and fish a ...
* Smoked fish
* Smoked meat
References
Further reading
*External links
{{Authority control Barbecue Cooking techniques Food preservation Culinary terminology